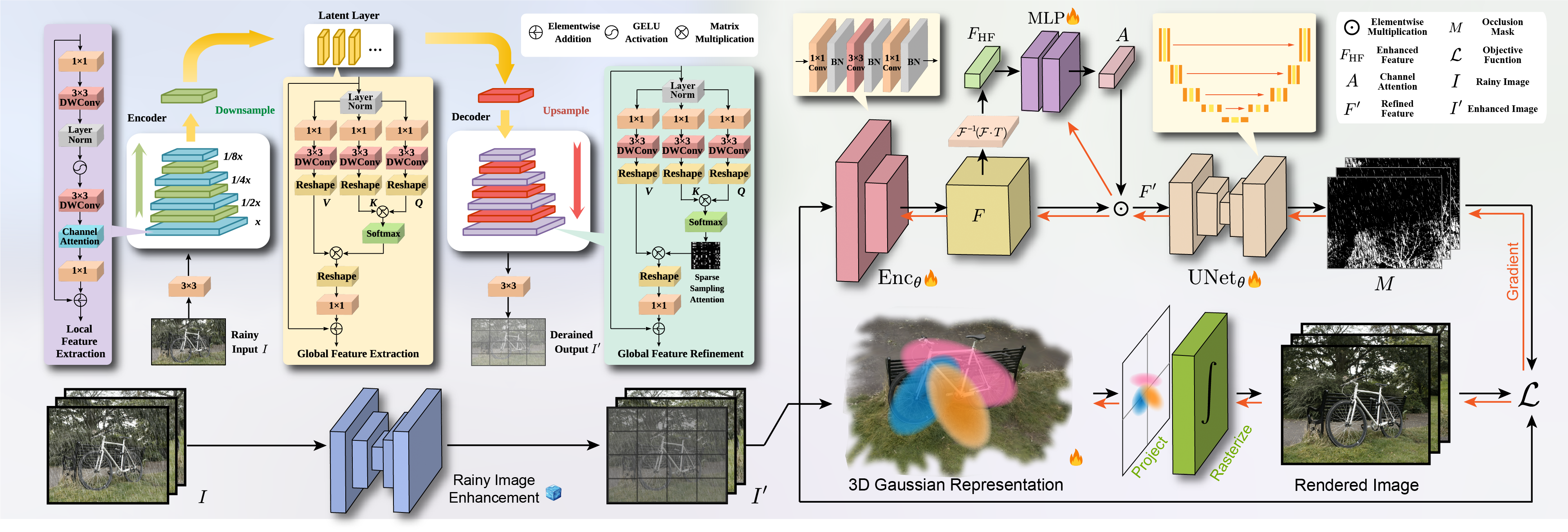
DeRainGS is designed for the task of 3D Reconstruction in Rainy Environments (3DRRE), aiming to reconstruct clear scenes in adverse weather conditions affected by raindrops and rain streaks.
Reconstruction under adverse rainy conditions poses significant challenges due to reduced visibility and the distortion of visual perception. These conditions can severely impair the quality of geometric maps, which is essential for applications ranging from autonomous planning to environmental monitoring. In response to these challenges, this study introduces the novel task of 3D Reconstruction in Rainy Environments (3DRRE), specifically designed to address the complexities of reconstructing 3D scenes under rainy conditions. To benchmark this task, we construct the HydroViews dataset that comprises a diverse collection of both synthesized and real-world scene images characterized by various intensities of rain streaks and raindrops. Furthermore, we propose DeRainGS, the first 3DGS method tailored for reconstruction in adverse rainy environments. Extensive experiments across a wide range of rain scenarios demonstrate that our method delivers state-of-the-art performance.
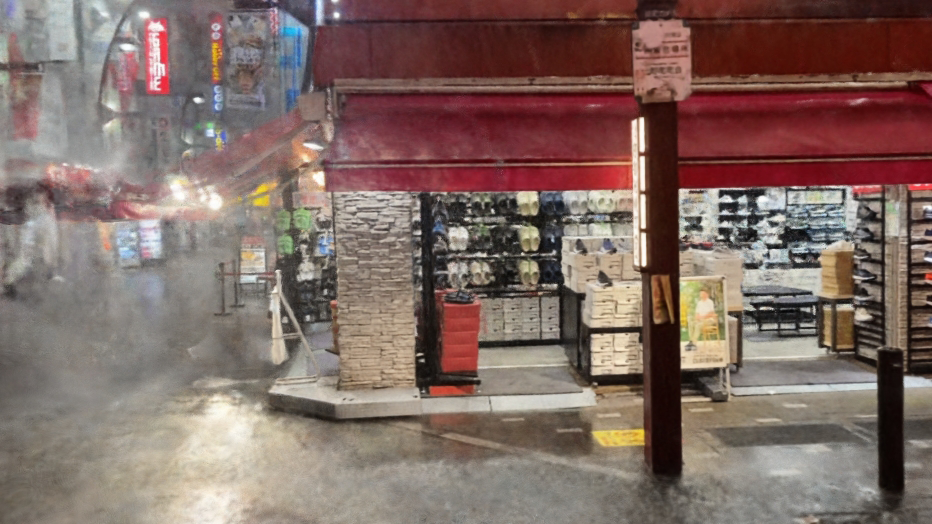
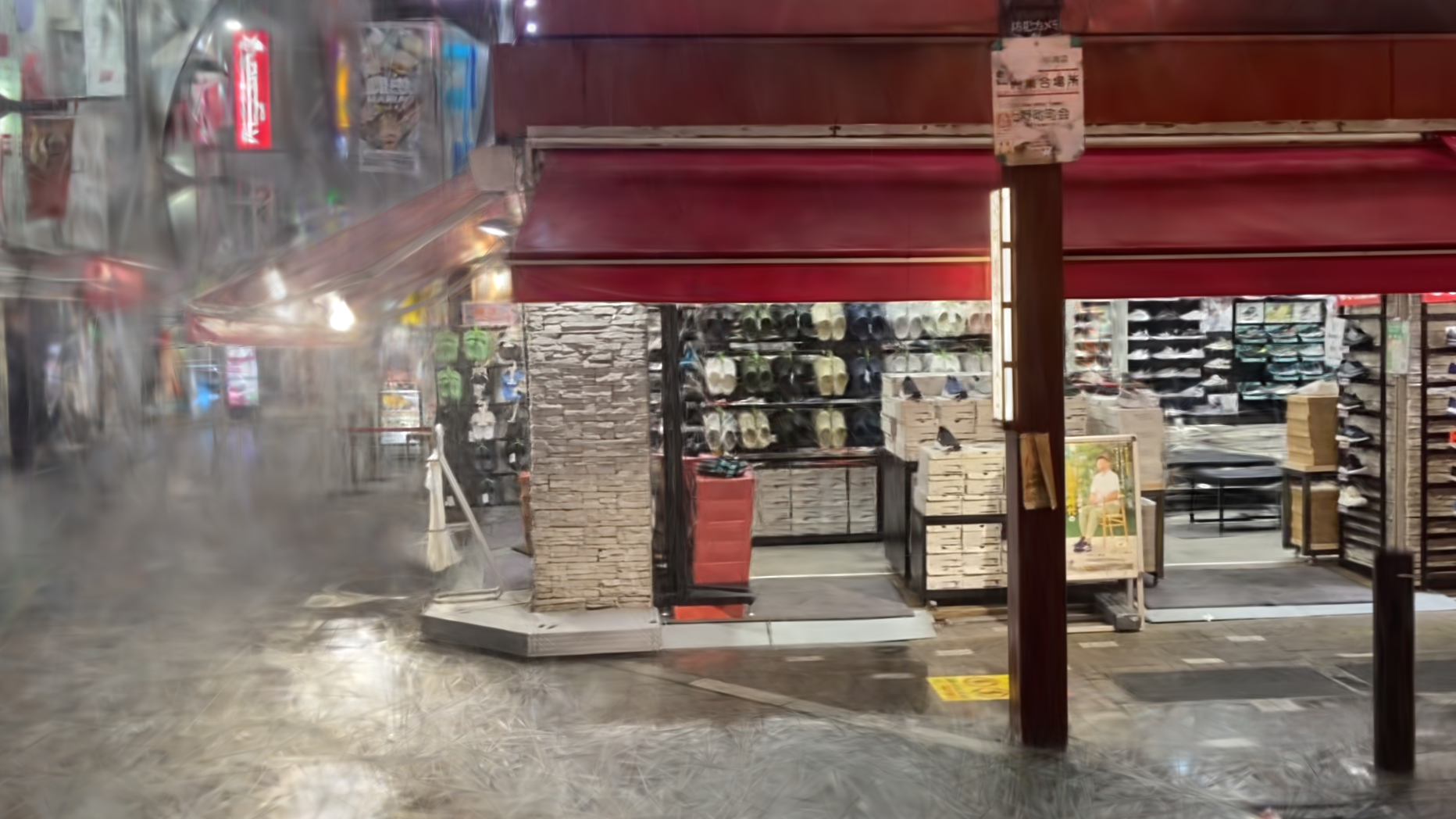
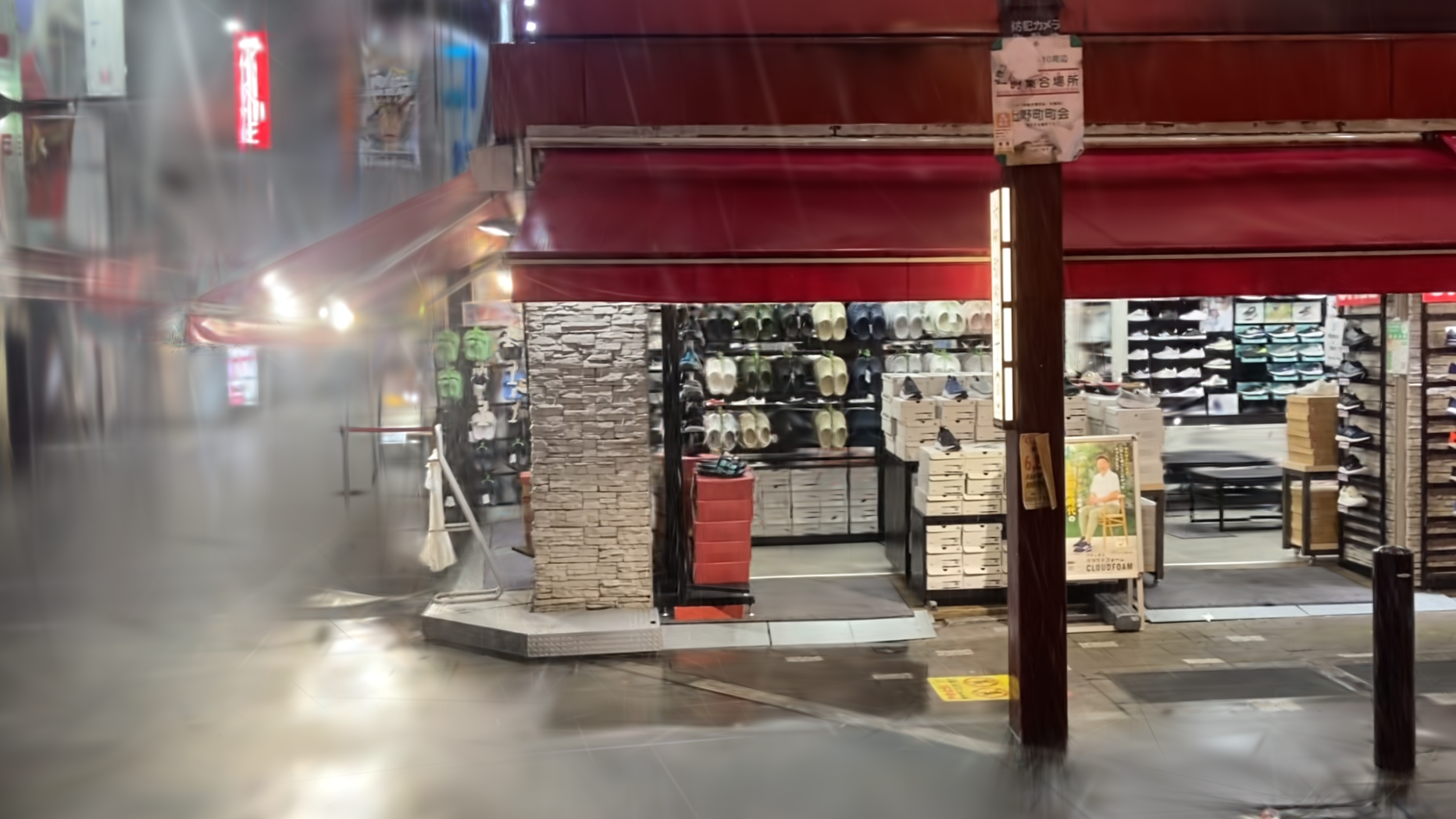
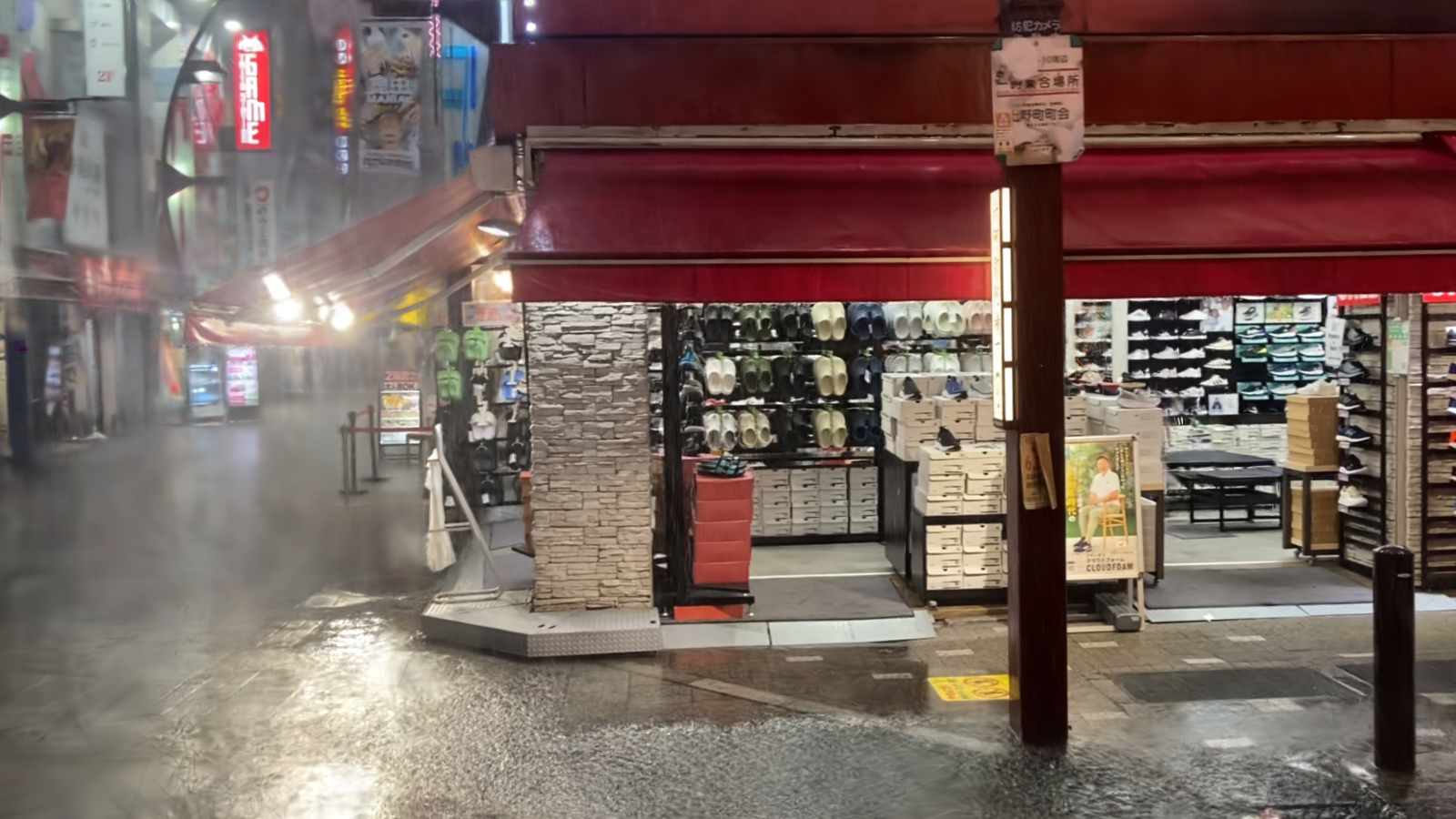
Our HydroViews dataset combines synthesized rain effects and real-world rainy scenes to provide comprehensive coverage of common rainy scenarios in real environments. Using a motion blur technique, we synthesize rain streaks to replicate the natural dynamics of rain, while raindrops are rendered with realistic transparency using Blender's fluid motion model. We also collect real-world collections of rainy scenes using a SONY-A7R3 camera, capturing images at a rate of one frame per second from various evening settings in Tokyo to enhance the visibility of rain streaks. Privacy is ensured by manually removing all identifiable personal elements from these scenes.
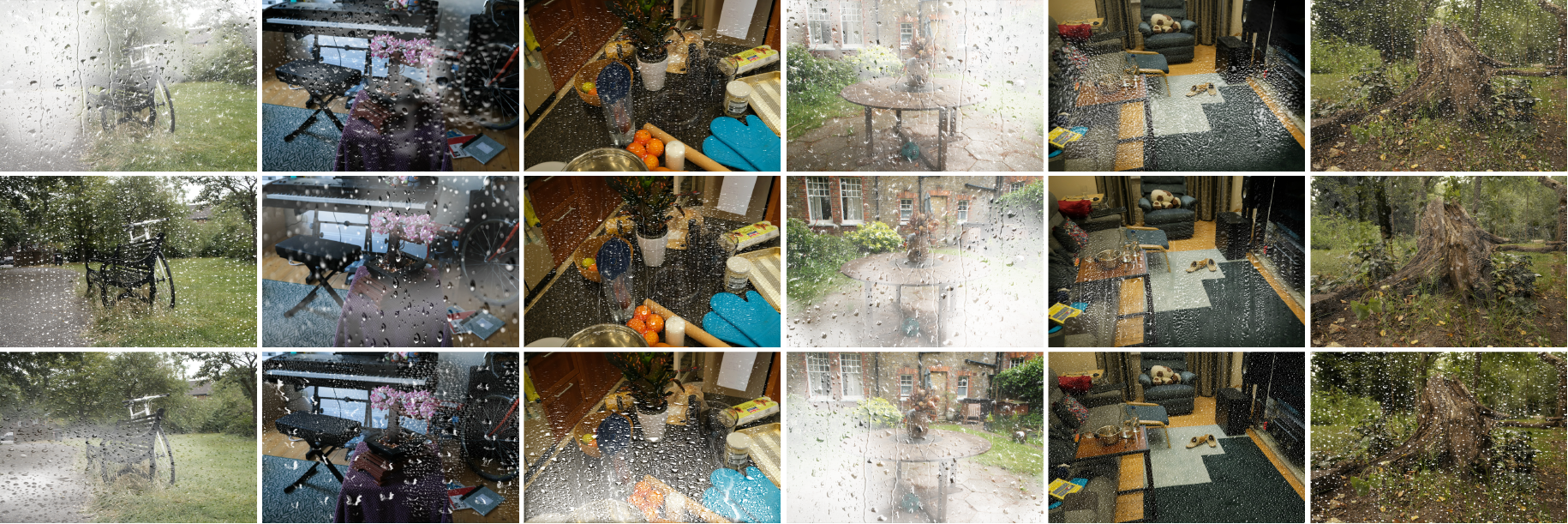


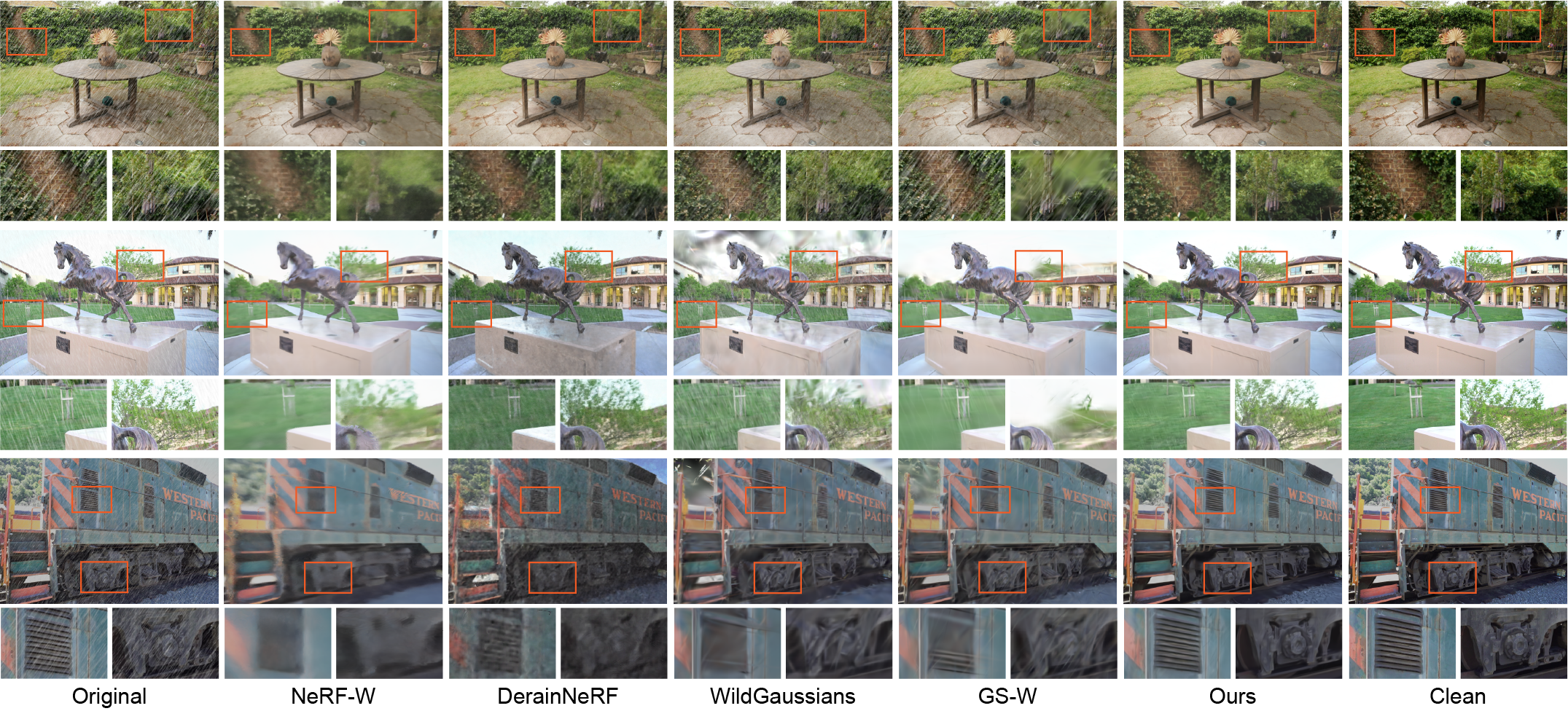
We compare DeRainGS with previous occlusion-free reconstruction and deraining baseline methods, including NeRF-W (Martin-Brualla, et al.), DerainNeRF (Li, et al.), WildGaussians (Kulhanek, et al.), and GS-W (Zhang, et al.), on the synthesized scenes of our HydroViews dataset.


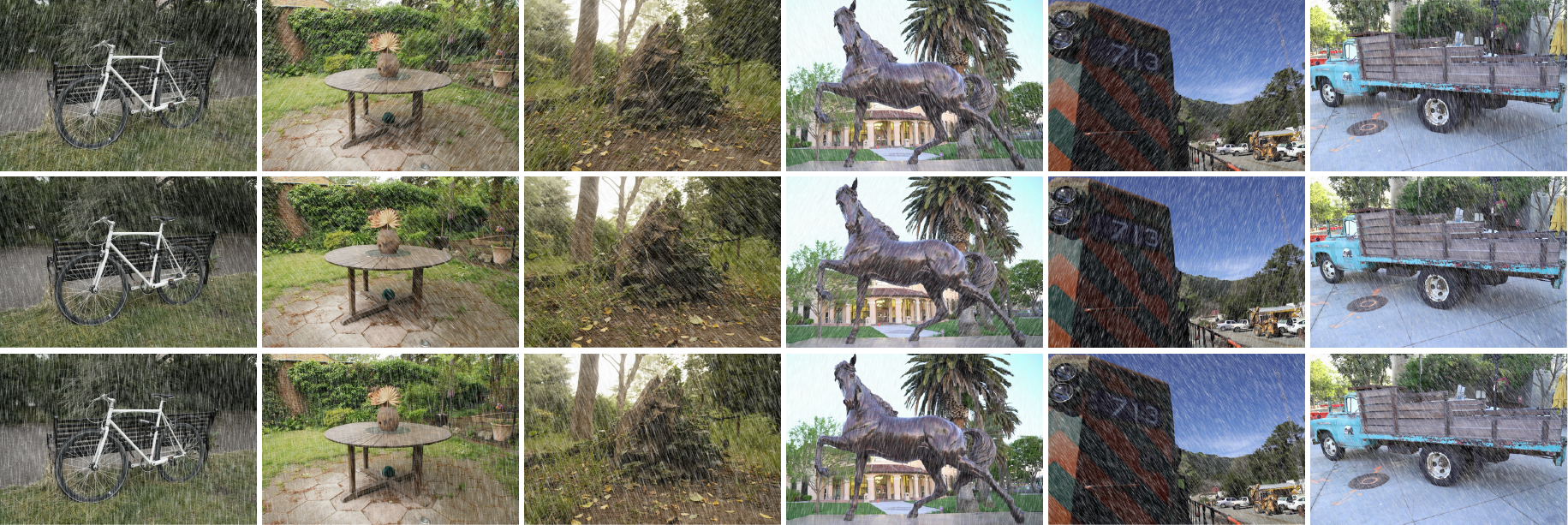
The visualizations below present synthesized videos from selected scenes featuring conditions of either rain streaks or raindrops. These compare the DeRainGS method with the vanilla 3DGS approach (Kerbl, et al.), showing how conventional reconstruction techniques often struggle with distortions and mist-induced occlusions caused by rain.
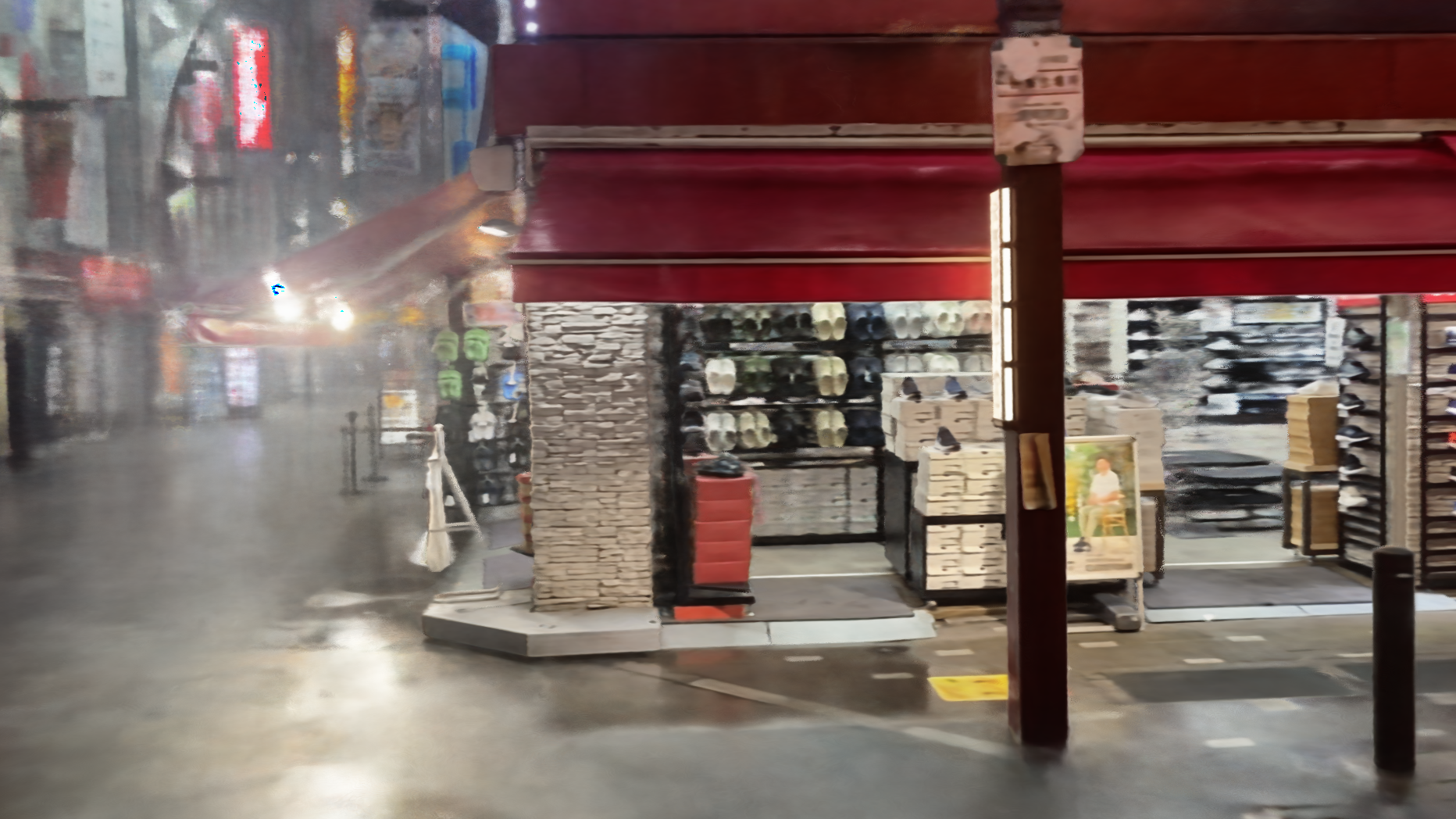
We demonstrate that our method can effectively generalize to real-world scenes, and compare it to the baseline methods mentioned above. The real-world scenes showing below are collected in our HydroViews dataset.





This website's template was designed based on the WildGaussians's page. The video comparison tool is from Ref-NeRF, and the image comparison tool is from Neuralangelo. The 3DGS viewer was developed using splatviz. We extend our sincere gratitude for their exceptional work and open-sourced codes. DeRainGS is built on the foundation of 3DGS; please adhere to the 3DGS license. We are thankful to all the authors for their outstanding contributions.
The orginal data for MipNeRF360 and tank & template benchmark are copyrighted by their respective owners. The rainy benchmark data presented on this website is copyright by us and is released under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) License. Under this license, you are permitted to copy, distribute, and transmit the data through any medium or format, as well as to modify and utilize the data for any purpose, including commercial. These rights cannot be withdrawn provided you adhere to the terms of the license.
@article{liu2024deraings,
title={DeRainGS: Gaussian Splatting for Enhanced Scene Reconstruction in Rainy Environments},
author={Liu, Shuhong and Chen, Xiang and Chen, Hongming and Xu, Quanfeng and Li, Mingrui},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.11540},
year={2024}
}